Pilot’s Quick Thinking Saves Robinson R22 Helicopter After Rotor Pedal Fail

What happened to cause the R22 tail rotor pedal fatigue failure?
A Robinson R22 helicopter’s right tail rotor pedal failed due to fatigue cracking during mustering operations, as found via ATSB (Australian Transport Safety Bureau) investigation details.
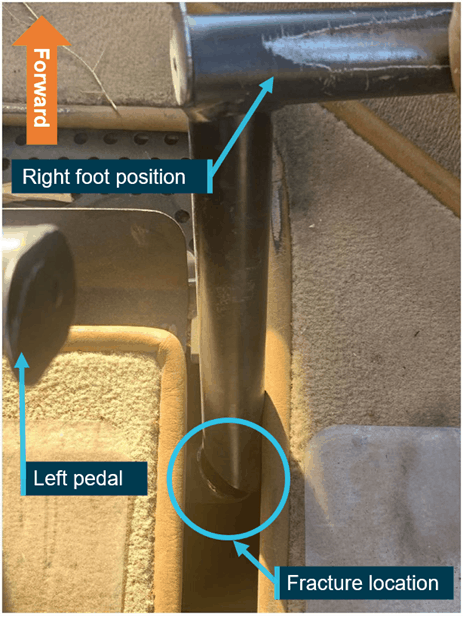
The R22 was conducting mustering at Kutchera Station in far north Queensland, Australia, on June 22, 2019, when the pilot applied a small amount of right pedal to turn the helicopter. The pedal cracked, bent forward, and became stuck.
The pilot was unable to dislodge the pedal and prepared for an immediate landing in accordance with the stuck pedal procedure.
However, just prior to landing, the helicopter struck a tree and became uncontrollable, impacting the ground. While the helicopter was substantially damaged, the pilot was uninjured.
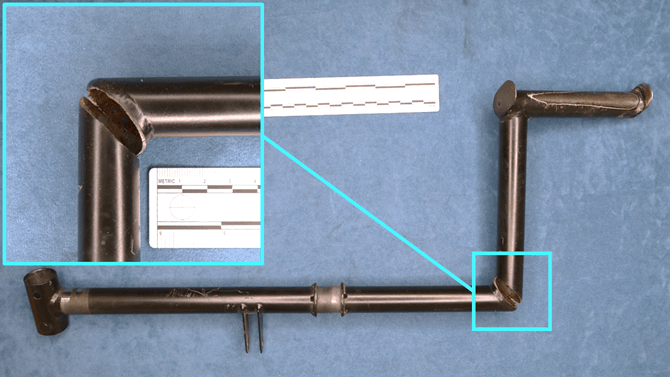
Following the accident, the helicopter’s maintenance organization identified a significant fracture in the right tail rotor pedal assembly at a right angle weld join between two sections of tube.
The right pedal was then sent to the ATSB’s technical facilities in Canberra
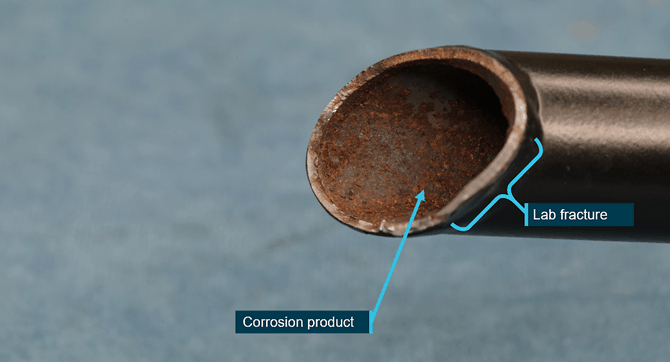
Examination and testing determined that the pedal fracture was a result of a preexisting fatigue failure, which had initiated at the highest stress part of the welded joint and had opened up following the control input applied by the pilot.
While it was considered likely that the developing crack was present at the time of a recent 100-hourly maintenance inspection, it was not detected, likely due to the location of the weld making it difficult to identify in-situ. The developing crack would have initially presented as a hairline feature, and it was located on a matte black surface, at a change in section slightly below the level of the cabin floor.
“The location of the fatigue crack in this accident highlighted the need to be vigilant when performing inspections in difficult or hard to reach places,” said acting Director Transport Safety Kerri Hughes.
“In the case of the tail rotor pedal, the inspection was made difficult due to the location, and required a torch and mirror to inspect the pedal assembly, which featured a matte black surface.”
While not required as part of the routine inspections, the helicopter’s maintenance organization has added the tail rotor pedals to the list of components that undergo magnetic particle inspection at each 2,200‑hour overall for the R22.
The investigation also notes the pilot’s positive actions likely contributed to their avoiding any injuries.
“The quick thinking actions of the pilot following the failure resulted in a good outcome, with no injuries sustained,” Ms Hughes said.
Key points:
- Pedal breaks, jams following small control input
- Failure likely due to a pre-existing fatigue crack, undetected at previous 100-hourly inspection
- Maintenance organization to conduct magnetic particle inspection of pedal assembly at 2,200-hourly major overhauls
What has been done as a result?
As a result of this accident, the maintenance provider has advised that, although not required by the maintenance manual, the tail rotor pedal assembly will now be included with other components that are sent for magnetic particle inspection at every 2,200-hourly overhaul.
Safety message
The location of the fatigue crack in this accident highlighted the need to be vigilant when performing inspections in difficult or hard to reach places. In the case of the tail rotor pedal, the inspection was made difficult due to the location, and required a torch and mirror to inspect a matte black surface.
Additionally, the quick thinking actions of the pilot following the failure resulted in a good outcome, with no injuries reported.
Read the full ATSB investigation report.
Equipment reliability professionals need great troubleshooting and root cause analysis skills
What are the biggest problems finding the root causes of equipment failures and equipment reliability issues? First, if you don’t do good troubleshooting to start with, you will lose the evidence you need to identify the failure’s root causes. That’s why we worked with equipment reliability expert Heinz Bloch to develop the Equifactor® Troubleshooting Tables. They can help your equipment experts or mechanics do a great job troubleshooting equipment problems and collecting the information you need for root cause analysis. To that regard, the tables can be customized to your unique problem. Learn more about Equifactor® here and take a look at how the Equifactor® courses can help you and your team.
Second, equipment reliability experts know a lot about the equipment, but they don’t usually know about human factors. The TapRooT® Root Cause Analysis System will help guide equipment reliability experts to the root causes of equipment failures whether they are caused by mechanical failures or human errors.
Founded in 1988, the TapRooT® Root Cause Analysis System solves hurdles every investigator faces
TapRooT® Root Cause Analysis Training System takes an investigator beyond his or her knowledge to think outside the box. Backed with extensive research in human performance, incident investigation, and root cause analysis, TapRooT® is a global leader in improved investigation effectiveness and productivity, stopping finger-pointing and blame, improving equipment reliability, and fixing operating problems.

NOTE: The above picture was taken prior to the pandemic and does not reflect COVID-19 practices that are part of current TapRooT® courses.
TapRooT® Root Cause Analysis Training courses are taught all over the world
System Improvements, the creator of the TapRooT® System, has a team of investigators and instructors with years of extensive training ready to offer assistance worldwide.
If you are interested in learning how to stop repeat incidents, find a 2-Day or 5-Day course; or view the complete selection of TapRooT® courses. We are available to train you and your staff on-site at your workplace; Contact us to discuss your needs. You may also call us at 865.539.2139 to discuss any questions you may have.
Keep in touch to improve your problem-solving skills
We’re continually training, helping you improve your professional root cause analysis skills. Stay current with your TapRooT® Root Cause Analysis skills and training through:
- Following our blog;
- Free newsletters;
- Tuning in to TapRooT® TV Video Sessions or our podcasts;
- Connecting with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, Pinterest, LinkedIn, and YouTube;
- And our annual Global TapRooT® Summit. Registration is now open!



